Hybrid Solar System
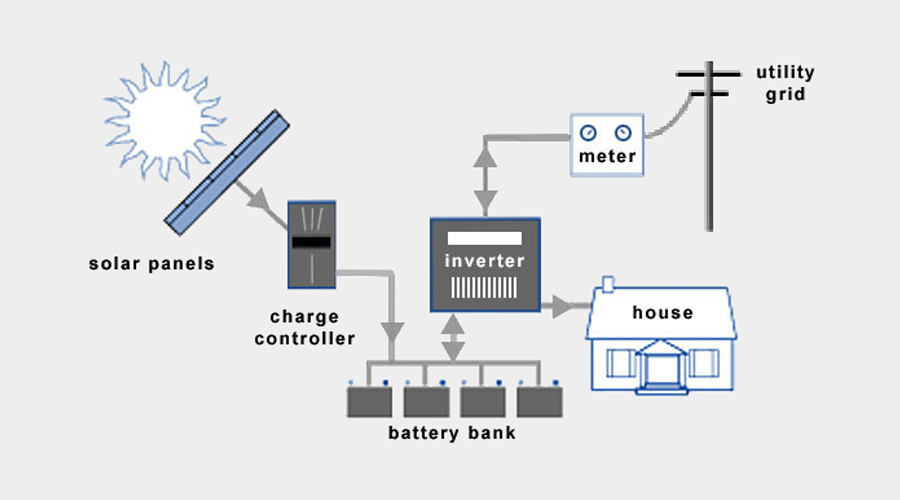
Hybrid solar systems combine the best from grid-tied and off-grid solar systems. These systems can either be described as off-grid solar with utility backup power, or grid-tied solar with extra battery storage.
If you own a grid-tied solar system and drive a vehicle that runs on electricity, you already kind of have a hybrid setup. The electrical vehicle is really just a battery with wheels.
Advantages of Hybrid Solar Systems
1. Less expensive than off-gird solar systems : Hybrid solar systems are less expensive than off-grid solar systems. You don’t really need a backup generator, and the capacity of your battery bank can be downsized. Off-peak electricity from the utility company is cheaper than diesel.
2. Smart solar holds a lot of promise The introduction of hybrid solar systems has opened up for many interesting innovations. New inverters let homeowners take advantage of changes in the utility electricity rates throughout the day.
Solar panels happen to output the most electrical power at noon – not long before the price of electricity peaks. Your home and electrical vehicle can be programmed to consume power during off-peak hours (or from your solar panels).
Consequently, you can temporarily store whatever excess electricity your solar panels in batteries, and put it on the utility grid when you are paid the most for every kWh. Smart solar holds a lot of promise. The concept will become increasingly important as we transition towards the smart grid in the coming years.
Equipment for Hybrid Solar Systems
Typical hybrid solar systems are based on the following additional components:
- – Charge Controller
- – Battery Bank
- – DC Disconnect (additional)
- – Battery-Based Grid-Tie Inverter
- – Power Meter
Battery-Based Grid-Tie Inverter
Hybrid solar systems utilize batter-based grid-tie inverters. These devices combine can draw electrical power to and from battery banks, as well as synchronize with the utility grid.
The bottom line is this: Right now, for the vast majority of homeowners, tapping the utility grid for electricity and energy storage is significantly cheaper and more practical than using battery banks and/or backup generators.